In the realm of dental health care, the significance of sterilization cannot be overstated. Dental laboratories, where prosthetics, braces, crowns, and various dental devices are crafted, are vital components of the dental care ecosystem. These environments require stringent sterilization protocols to ensure the safety and well-being of patients and dental professionals alike. Here’s more about sterilization techniques used and why proper sterilization techniques in a dental laboratory are an absolute necessity.
Sterilization Techniques
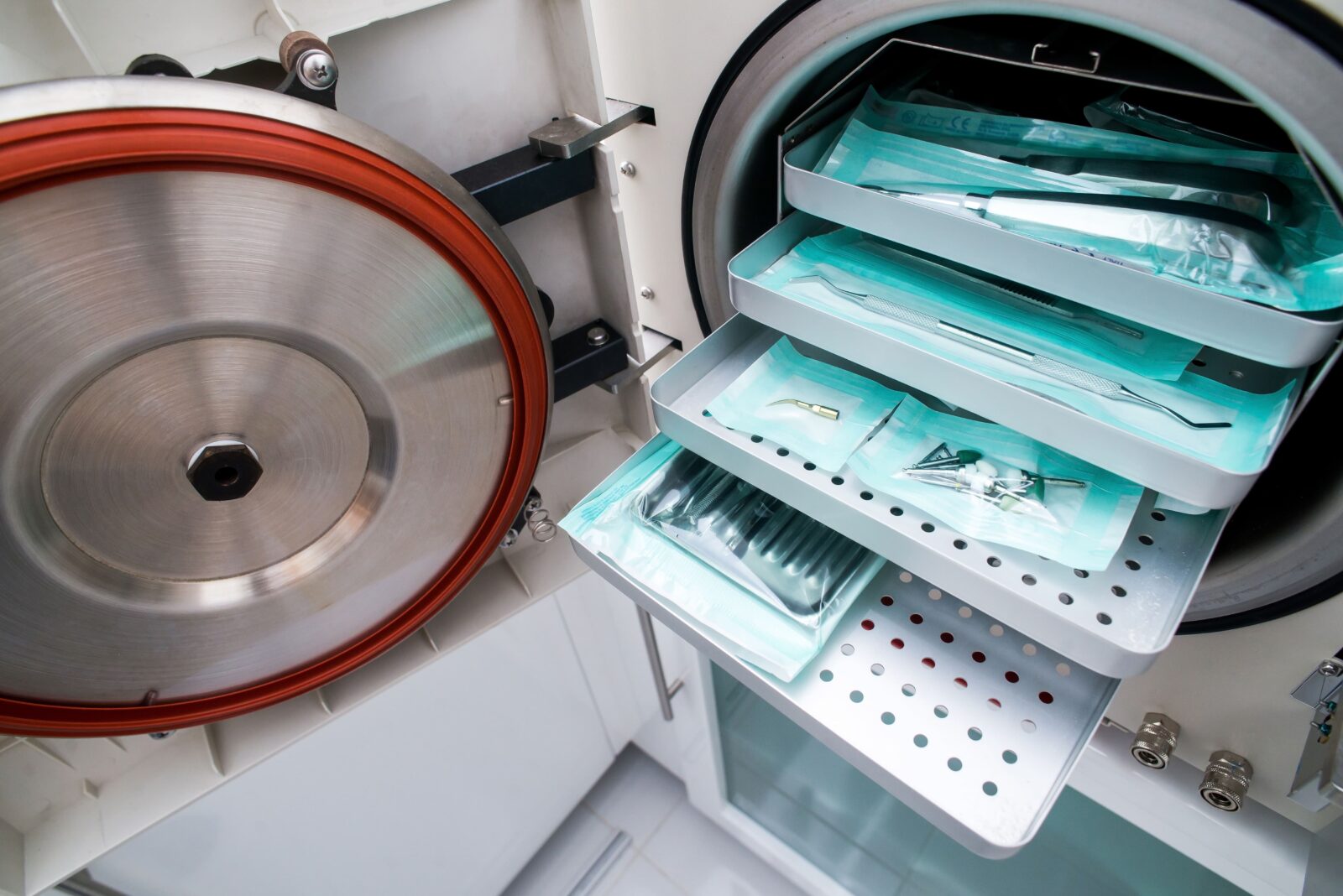
Dental laboratories employ various sterilization techniques to ensure that all instruments, equipment, and dental prosthetics are free from microbial contamination before being used on patients. These techniques are designed to kill or remove all forms of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. Here are some of the most common sterilization methods used in dental laboratories:
| Sterilization Technique | Method | Applications |
| Autoclaving (Steam Sterilization) | High-pressure saturated steam at 121-134°C | Metal instruments, certain dental prosthetics |
| Dry Heat Sterilization | Hot air at 160-180°C | Metal instruments, some dental prosthetics |
| Chemical Vapor Sterilization | Chemicals heated under pressure to create sterilizing vapor | Metal instruments, some dental devices |
| Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization | Ethylene oxide gas | Heat-sensitive and moisture-sensitive items |
| Ultraviolet (UV) Light Sterilization | Ultraviolet light exposure | Surface disinfection, air purification |
| Ultrasonic Cleaning (Pre-sterilization) | High-frequency sound waves in cleaning solution | Pre-cleaning of instruments |
The Importance of Sterilization
Ensuring Patient Safety
The primary goal of sterilization in dental laboratories is to protect patients from infections. Dental devices and prosthetics must be free from harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi before they can be safely used. Inadequate sterilization can lead to the transmission of infectious diseases, posing serious health risks to patients. By implementing rigorous sterilization protocols, dental laboratories can significantly reduce the risk of cross-contamination and infection, safeguarding patient health.
Maintaining High Quality Standards

Sterilization is integral to maintaining high-quality standards in dental laboratory output. Contamination of dental appliances not only poses health risks but can also compromise the structural integrity and functionality of these devices. Proper sterilization ensures that the materials used in dental appliances retain their desired properties and function as intended, thereby maintaining the high standards expected in dental care.
Compliance with Regulations
Dental laboratories are subject to stringent regulatory standards that dictate the methods and efficacy of sterilization processes. Compliance with these regulations is not optional; it is a legal requirement. By adhering to approved sterilization techniques, dental laboratories ensure they meet industry standards and avoid potential legal and financial repercussions associated with non-compliance.
Promoting a Safe Work Environment
The benefits of sterilization extend beyond patient safety to include the health and safety of dental laboratory technicians and other staff members. Proper sterilization techniques minimize the risk of occupational exposure to infectious agents, creating a safer work environment. This not only protects employees but also fosters a culture of safety and responsibility within the laboratory.
Enhancing Laboratory Efficiency
Efficient sterilization processes streamline laboratory operations, reducing the risk of errors and rework. By implementing effective sterilization protocols, dental laboratories can ensure that equipment and instruments are ready for use when needed, enhancing overall productivity. Moreover, efficient sterilization can extend the lifespan of dental instruments and equipment, providing long-term cost savings.
Building Trust with Dental Practices
Dental laboratories that prioritize sterilization demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety. This commitment builds trust with dental practices and patients, establishing the laboratory as a reliable partner in dental care. In a competitive industry, a reputation for stringent sterilization practices can be a significant differentiator.
Conclusion
Proper sterilization techniques in dental laboratories are not just a regulatory requirement; they are a cornerstone of patient safety, quality care, and professional responsibility. By investing in effective sterilization protocols, dental laboratories play a crucial role in preventing infections, maintaining high-quality standards, and fostering trust within the dental community. As dental technology evolves, so too must the approaches to sterilization, ensuring that dental laboratories remain at the forefront of patient care and safety.