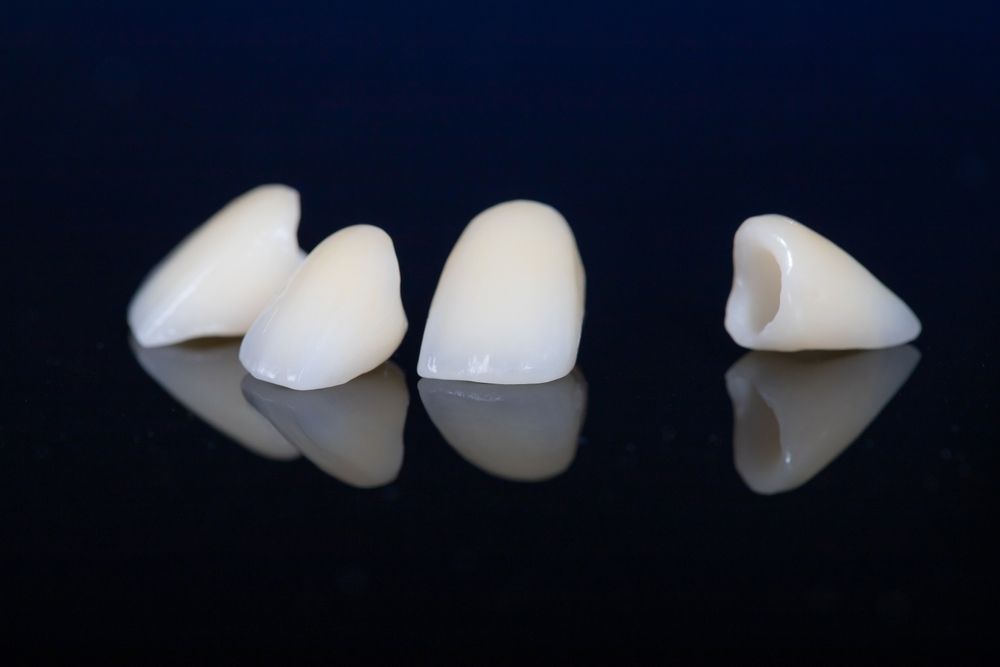
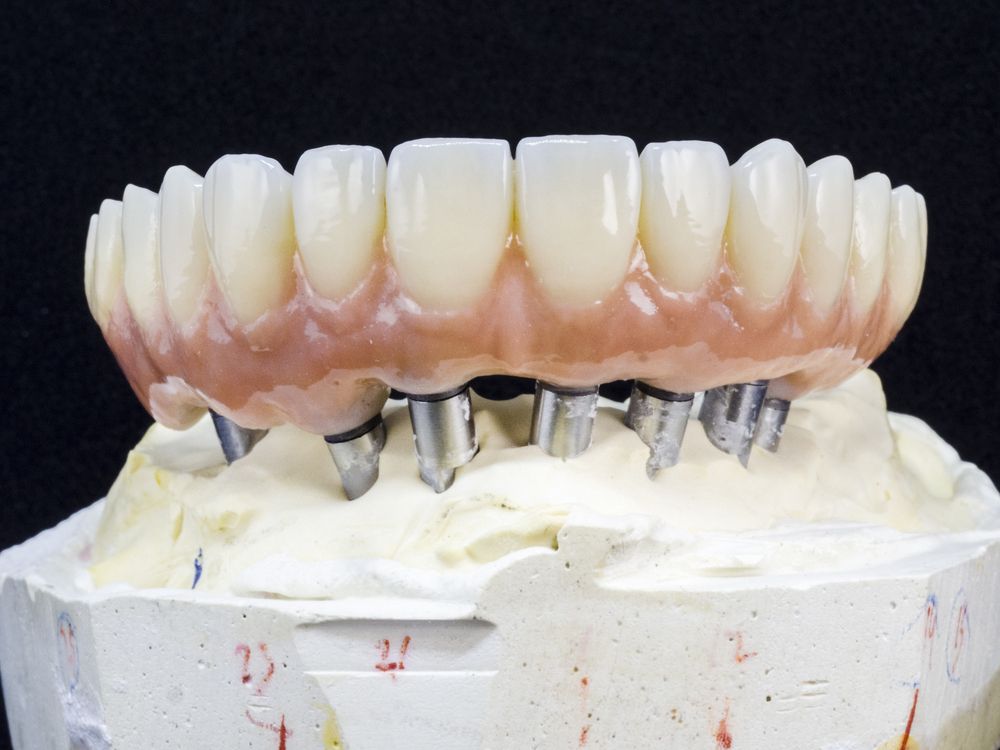
In the ever-evolving landscape of dental technology, the rise of 3D printing has marked a revolutionary shift, heralding a new era of precision, efficiency, and customization in dental lab operations. This cutting-edge technology, once a speculative fiction, is now at the forefront of dental practice, offering unparalleled benefits in the creation of dental prosthetics, orthodontic devices, and surgical guides. As dental laboratories stand on the cusp of this technological revolution, the integration of 3D printing into their services not only promises to enhance the quality of dental care but also to redefine the standards of patient satisfaction and lab productivity. This blog aims to delve into the transformative potential of 3D printing technology in dental labs, exploring its applications, benefits, and the practical steps labs can take to embrace this innovative technology, ensuring they remain at the leading edge of the dental industry.
Understanding 3D Printing in Dentistry
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that builds three-dimensional objects from digital models by layering material. In dentistry, this technology has become a game-changer, offering a range of applications from the production of intricate dental prosthetics to the creation of custom surgical guides. There are several types of 3D printing technologies utilized in the dental field, including Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), each with its unique advantages and suitability for different dental applications.
The benefits of 3D printing in dental lab operations are profound. Customization is at the forefront, as 3D printing allows for the creation of dental appliances and prosthetics tailored to the individual anatomy of each patient, enhancing comfort and fit. Speed is another significant advantage, with 3D printing capable of producing items in a fraction of the time required for traditional manufacturing methods. This efficiency can greatly reduce waiting times for patients and increase the productivity of dental labs. Moreover, 3D printing has been found to be cost-effective, reducing waste and the need for expensive tooling or molds traditionally used in dental manufacturing.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dental Labs
The scope of 3D printing in dental laboratories is extensive, touching almost every aspect of dental care. Crowns, bridges, and veneers can now be printed with remarkable precision, ensuring a perfect fit and reducing the need for adjustments. Complete and partial dentures, as well as orthodontic devices such as aligners and retainers, are produced with a level of customization previously unattainable, significantly improving patient comfort and treatment outcomes.
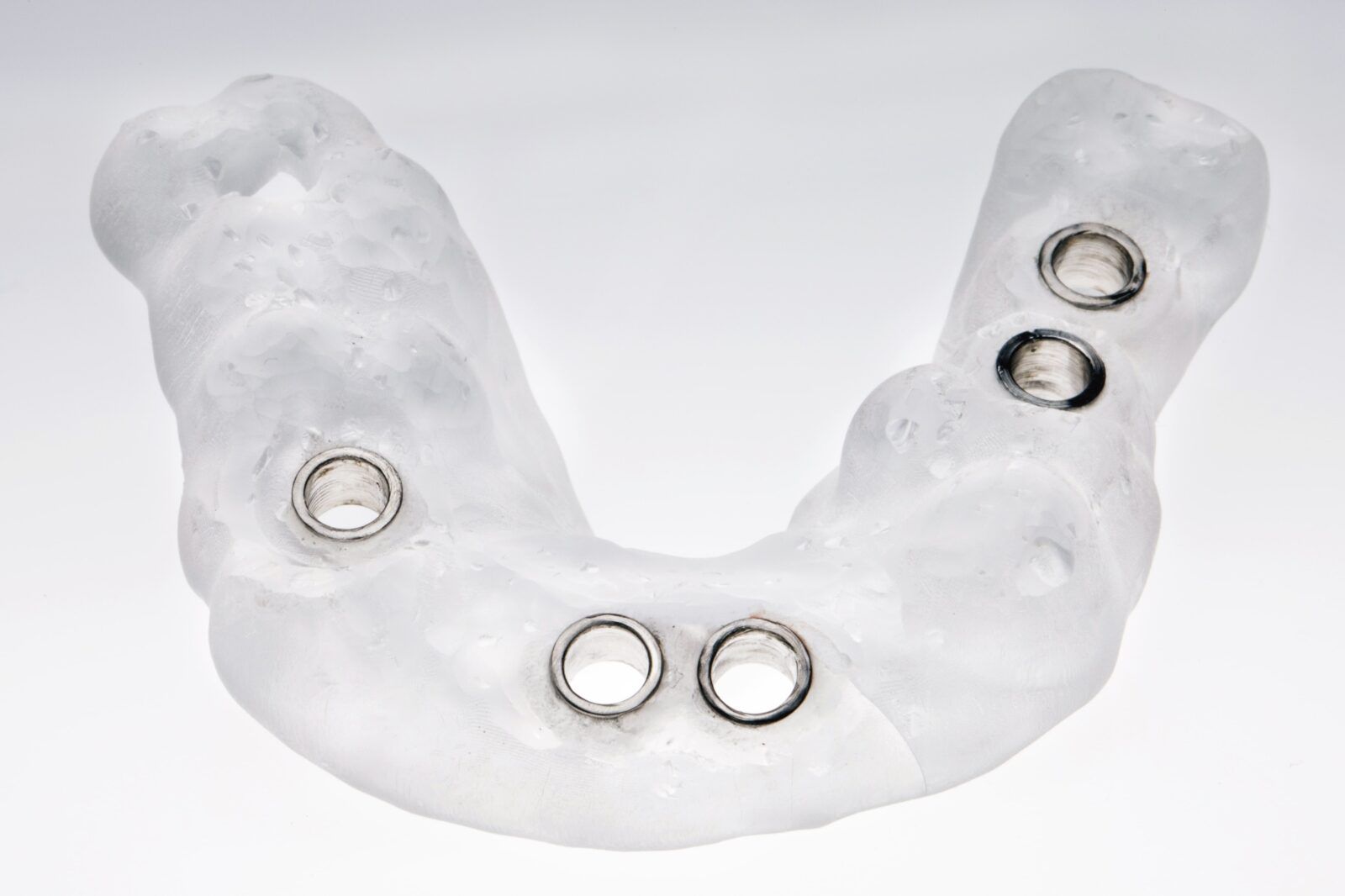
Surgical guides for implant placement are another area where 3D printing shines, enabling surgeons to execute procedures with enhanced accuracy and confidence. The ability to pre-plan surgeries in a virtual environment and print precise guides tailored to the patient’s anatomy has revolutionized dental surgery, minimizing risks and improving recovery times.
Beyond these applications, 3D printing also extends to the creation of models for patient education and treatment planning, as well as the production of tools and jigs that assist in the dental lab workflow. The adoption of 3D printing technology in dental labs not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also opens up new possibilities for innovative treatments and services.
The transition to 3D-printed dental products has not only demonstrated comparable quality to traditional methods but, in many cases, has surpassed it. Advances in materials and printing technology have resulted in products that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also exhibit superior strength and durability. As dental professionals continue to embrace and refine 3D printing techniques, the gap between traditional and digital dental lab technologies continues to narrow, heralding a new era of high-quality, patient-centered dental care.
Steps for Incorporating 3D Printing into Dental Labs
Incorporating 3D printing technology into dental laboratories requires a strategic approach, focusing on equipment, training, workflow integration, and regulatory compliance. The first step is selecting the right 3D printer, which depends on the specific applications it will be used for, such as prosthetics, orthodontics, or surgical guides. Essential considerations include print resolution, material compatibility, speed, and cost. Alongside the printer, labs must invest in high-quality scanning equipment and software for designing and modeling dental appliances.
Training and skill development for lab technicians are paramount to successfully integrate 3D printing into dental lab operations. Technicians must be proficient in digital design software and understand the nuances of the printing process to ensure high-quality outcomes. Many equipment manufacturers and professional organizations offer specialized training programs designed to equip dental professionals with the necessary skills.
Integrating 3D printing into existing lab workflows may require reevaluation of current processes to identify where and how 3D printing can add the most value. This might involve streamlining the transition from digital scans to printed models, ensuring seamless communication between dental offices and the lab, and optimizing the post-processing and quality control of printed items.
Regulatory considerations are also critical, as dental products must meet stringent standards set by health authorities. Labs must stay informed about the regulations governing the use of 3D-printed dental appliances and materials, ensuring compliance to maintain the safety and efficacy of their products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of 3D printing technology into dental laboratories represents a significant leap forward in the field of dentistry. By embracing this advanced technology, dental labs can dramatically enhance the efficiency, precision, and customization of dental appliances, thereby elevating the standard of patient care. The journey towards fully integrating 3D printing involves navigating challenges such as equipment selection, training, workflow adaptation, and compliance with regulatory standards. However, the potential rewards—ranging from streamlined operations to the ability to offer innovative dental solutions—are immense. As we look to the future, it is clear that 3D printing will continue to revolutionize dental lab practices, driving the industry towards new horizons of innovation and excellence. Dental labs that adapt to incorporate this technology will not only stay competitive but also play a pivotal role in shaping the future of dental care.