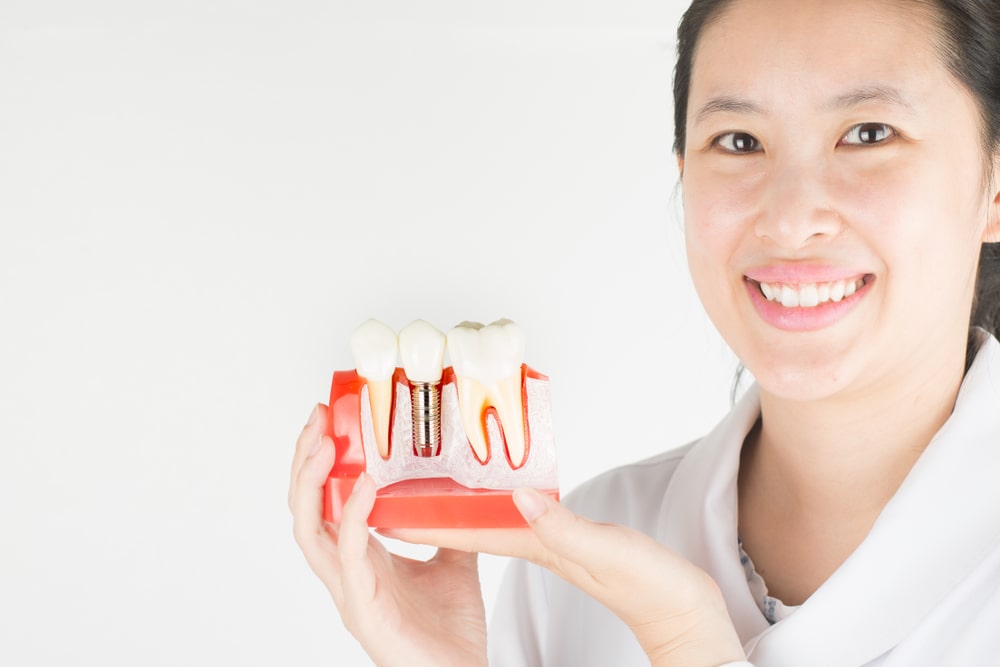
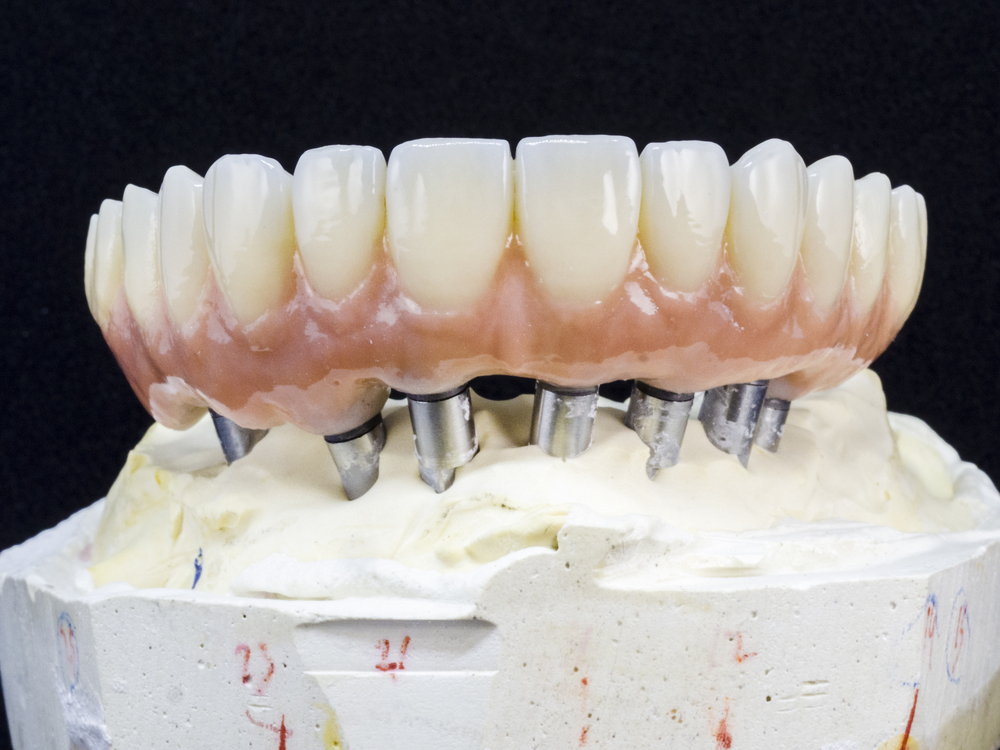
Implant-supported full-arch restorations represent a groundbreaking solution for patients suffering from severe tooth loss. These restorations provide a stable, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional dentures, enhancing both functionality and quality of life. By securely anchoring a full set of prosthetic teeth to dental implants, this advanced procedure restores the natural look and feel of a complete smile. The fabrication process of these restorations involves a meticulous blend of cutting-edge technology and skilled craftsmanship, ensuring each patient receives a custom-made solution tailored to their unique needs. In this blog, we will delve into the comprehensive steps involved in creating implant-supported full-arch restorations, highlighting the critical role dental labs play in transforming smiles and lives.
Comprehensive Steps Involved in Creating Implant-Supported Full-Arch Restorations
1. Initial Consultation and Planning
- Patient Assessment: Dental professionals evaluate the patient’s oral health, bone density, and overall suitability for implants.
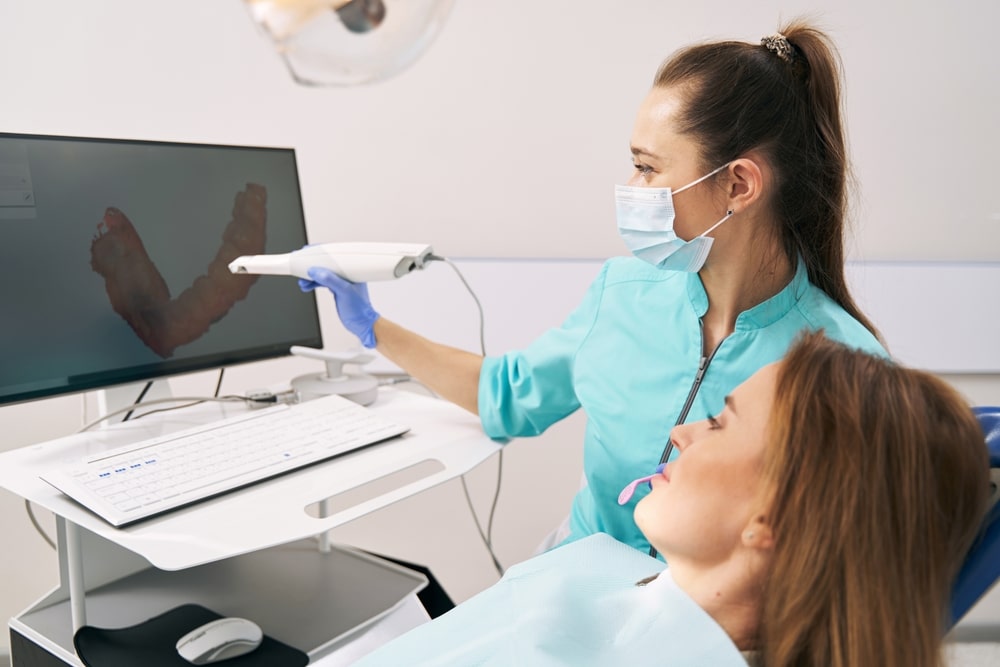
- Digital Imaging: Use of CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) scans and intraoral scanners to obtain detailed images of the patient’s oral structures.
- Treatment Planning: Collaboration between the dentist, oral surgeon, and dental lab to devise a personalized treatment plan.
2. Implant Placement
- Surgical Procedure: Placement of dental implants into the jawbone by an oral surgeon or periodontist.
- Healing Period: Allowing time for osseointegration, where the implants fuse with the bone, typically taking several months.
3. Impression Taking
- Traditional Impressions: Use of physical molds to capture the exact shape of the patient’s mouth.
- Digital Impressions: Utilization of intraoral scanners to create precise digital models.
4. Model Creation
- Physical Models: Creating stone or resin models from traditional impressions.
- Digital Models: Generating 3D digital models using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
5. Framework Design
- Initial Design: Designing the metal framework that will support the prosthetic teeth, using CAD software.
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials such as titanium or zirconia for durability and biocompatibility.
6. CAD/CAM Technology
- Digital Design: Using CAD software to refine the framework and prosthetic teeth design.
- Milling Process: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling machines carve the framework and teeth from high-strength materials.
- 3D Printing: Employing 3D printers for precise and efficient creation of components.
7. Customization and Aesthetics
- Shade Matching: Ensuring the color of the prosthetic teeth matches the patient’s natural teeth or desired shade.
- Layering Techniques: Applying ceramic layers to achieve a natural appearance.
- Finishing Touches: Polishing and glazing the restoration for a lifelike finish.
8. Final Fitting and Adjustment
- Try-In Appointment: Verifying the fit and appearance of the restoration in the patient’s mouth.
- Adjustments: Making any necessary adjustments for optimal comfort and function.
- Cementation/Attachment: Securing the restoration onto the implants, either permanently or with screws for removable options.
9. Post-Operative Care and Maintenance
- Patient Education: Providing comprehensive care instructions to ensure the longevity of the restoration.
- Regular Check-Ups: Scheduling follow-up appointments to monitor and maintain the restoration’s condition.
Role of Dental Labs
Dental labs are integral to the success of implant-supported full-arch restorations. They provide:
- Precision and Accuracy: Using advanced technology to create precise models and frameworks.
- Customization: Tailoring each restoration to meet the specific needs and preferences of the patient.
- Collaboration: Working closely with dental professionals to ensure seamless integration of clinical and laboratory processes.
- Quality Control: Ensuring high standards in materials and craftsmanship for durable and aesthetically pleasing results.
- Innovation: Continually adopting new technologies and techniques to improve outcomes and efficiency.
- Craftsmanship and Aesthetic Expertise: Skilled technicians apply their expertise in color matching, ceramic layering, and finishing to ensure that the final product not only functions well but also looks natural.
- Educational Support and Training: They provide insights and updates on new materials, technologies, and techniques, helping clinicians stay informed about the best practices in restorative dentistry. Additionally, labs may offer training sessions or workshops to demonstrate the latest advancements and their practical applications
Conclusion
The creation of implant-supported full-arch restorations is a complex and meticulous process that involves a seamless collaboration between dental professionals and dental labs. From the initial consultation and precise planning to the final fitting and customization, each step is crucial in ensuring the success and longevity of the restoration. Dental labs play a pivotal role in this process, leveraging advanced technologies and skilled craftsmanship to deliver high-quality, personalized solutions that restore both function and aesthetics to patients’ smiles. With the advancements in digital dentistry and materials science, implant-supported full-arch restorations have become a reliable and transformative option for those seeking a permanent solution to severe tooth loss. If you are considering this procedure, consult with your dental professional to learn more about how it can improve your quality of life.