As dental technology continues to advance, the way dentures are fabricated is undergoing a significant transformation. Traditional dentures, long the standard in prosthetic dentistry, are now being compared with innovative 3D printed alternatives that offer a streamlined digital workflow. For dentists, understanding the key differences between these two methods is essential for making informed decisions about patient care and practice efficiency. This blog explores how traditional and 3D printed dentures differ in terms of fabrication, materials, fit, and overall value, providing a practical comparison to help guide clinical choices.
In This Blog:
- Fabrication Process: Analog vs. Digital Workflow
- Material Considerations
- Fit and Functionality
- Chairside and Laboratory Time
- Cost and Accessibility
- Patient Experience and Satisfaction
- Future Trends in Denture Fabrication
Fabrication Process: Analog vs. Digital Workflow
Traditional Dentures rely on a multi-step, manual process that often begins with physical impressions, followed by bite registration, wax try-ins, and final processing with hand-packed acrylic. Each step requires a high level of technical skill and patient cooperation. Multiple appointments are typically needed to achieve a proper fit, and even minor adjustments can mean additional lab work and turnaround time.
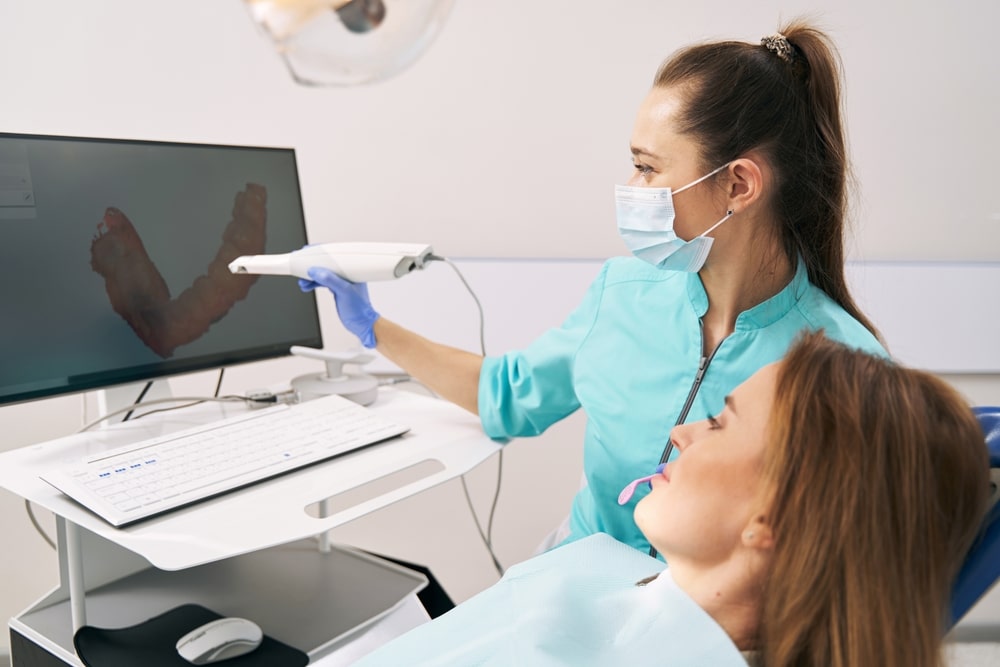
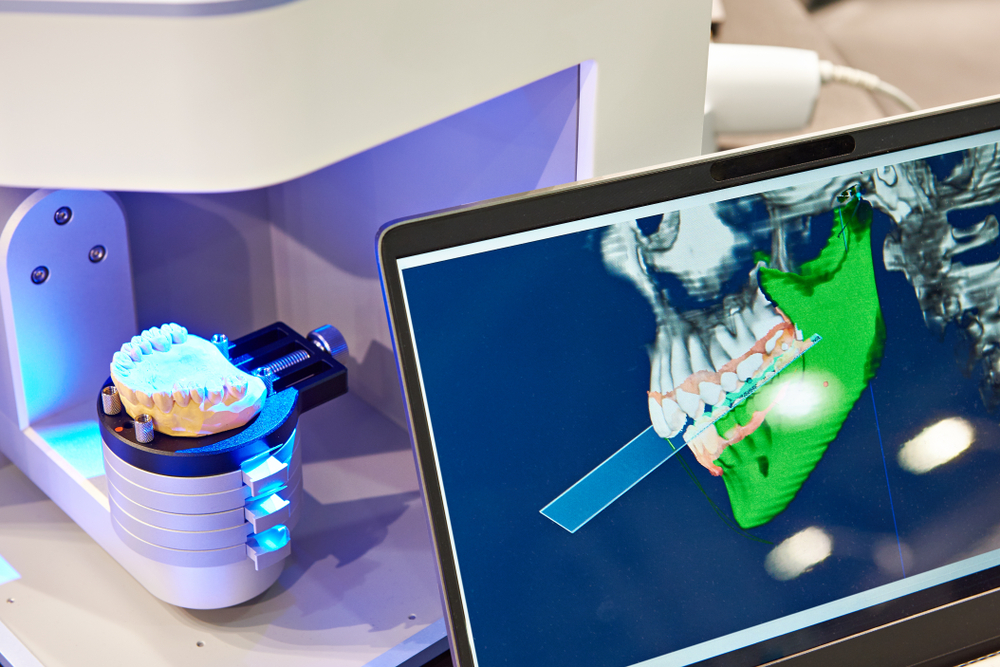
3D Printed Dentures, on the other hand, utilize a digital workflow that begins with an intraoral scan or digitized impression. The data is used to design the denture using CAD software, and the final prosthesis is fabricated via a 3D printer. This process allows for increased efficiency and consistency. In many cases, digital dentures can be designed, printed, and delivered in fewer appointments, reducing chair time and improving patient satisfaction.
Material Considerations
In traditional dentures, polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) has been the go-to material for decades due to its affordability, ease of processing, and satisfactory esthetic properties. However, the layering and curing processes are subject to human error, which can affect long-term durability and fit.
3D printed dentures utilize advanced printable resins specifically engineered for strength, flexibility, and aesthetics. These materials are designed to be biocompatible and offer predictable results with minimal shrinkage or distortion. While some clinicians remain cautious about the long-term wear resistance of printed materials, ongoing improvements in resin formulations continue to enhance their reliability in clinical settings.
Fit and Functionality
Achieving an optimal fit with traditional dentures depends heavily on the skill of both the dentist and the lab technician. Minor inaccuracies during impression-taking or acrylic processing can lead to issues like poor retention, pressure points, or uneven occlusion. While experienced labs can produce excellent results, there is inherent variability in analog techniques.
3D printed dentures offer a higher level of precision thanks to digital design and automated production. The digital workflow allows for fine-tuning of the fit and occlusion before fabrication, and the final printed prosthesis often requires fewer post-insertion adjustments. Consistency across cases is improved, which can lead to better patient comfort, enhanced chewing function, and reduced chairside time for modifications.
Chairside and Laboratory Time
Traditional denture fabrication is often time-intensive, requiring several appointments for impressions, try-ins, and final delivery. The lab work involved is laborious, and adjustments or remakes can further delay the process. For busy dental practices, this can limit efficiency and patient turnover.
With 3D printed dentures, digital impressions and virtual design significantly reduce the time required for both clinical and laboratory steps. The streamlined workflow allows many cases to be completed in as little as two appointments. Additionally, digital files can be stored for easy reproduction or future adjustments, eliminating the need to restart the process in case of loss or damage.
Cost and Accessibility
Traditional dentures have a relatively low initial material cost, and many practices are already equipped for analog fabrication and adjustments. However, the cumulative expenses, such as labor, chair time, remakes, and extended turnaround, can add up, especially in high-volume settings. For smaller practices or those without in-house lab support, outsourcing can further drive up costs and extend delivery times.
3D printed dentures, while requiring an upfront investment in digital equipment and training, offer long-term cost advantages. Digital workflows reduce manual labor and remake rates, allowing for faster production and more predictable outcomes. Over time, practices and labs that adopt 3D printing often report increased efficiency, better scalability, and improved patient throughput, making the technology more accessible and cost-effective in the long run.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction
From the patient’s perspective, traditional dentures can deliver excellent aesthetics and function, particularly when crafted by skilled technicians. However, the lengthy treatment process, frequent adjustments, and discomfort from imperfect fits may negatively impact the overall experience.
3D printed dentures offer a more modern and patient-friendly experience. Digital impressions are less invasive than traditional molds, and fewer appointments mean less disruption to the patient’s schedule. Additionally, the precision of digital design typically results in a better initial fit, minimizing the need for post-insertion adjustments. The ability to quickly reproduce or reprint dentures using stored digital files is also a major benefit for patients who lose or damage their prosthesis.
Future Trends in Denture Fabrication
The future of denture production is undeniably digital. As 3D printing technology evolves, we are seeing rapid improvements in printable materials, software capabilities, and hybrid workflows that combine 3D printing with milling or injection molding. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also beginning to play a role in automating denture design, further enhancing accuracy and reducing turnaround time.
In addition, the ability to integrate 3D printing with other digital dentistry tools, such as intraoral scanners, virtual articulators, and patient-specific smile design software, promises a more personalized and efficient approach to prosthodontics. As adoption rates grow and costs continue to decline, 3D printed dentures are expected to become the new standard in removable prosthetic care.
Conclusion
The shift from traditional to 3D printed dentures represents a major advancement in dental prosthetics, offering clear benefits in accuracy, efficiency, patient satisfaction, and long-term value. While traditional methods still have their place, particularly in certain clinical situations, the advantages of digital workflows are becoming increasingly difficult to ignore. For dentists and labs alike, understanding these differences is key to delivering optimal care and staying competitive in a rapidly evolving field.
Ready to elevate your denture offerings? Partner with Pan-Am Dental Lab to explore how 3D printed dentures can improve fit, function, and efficiency for your patients.