Implant dentistry has seen remarkable advancements over the years, with digital radiography emerging as a pivotal technology. This modern approach to imaging offers numerous benefits, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and patient care. In this blog, we delve into the uses and advantages of digital radiography in implant dentistry.
What is Digital Radiography?
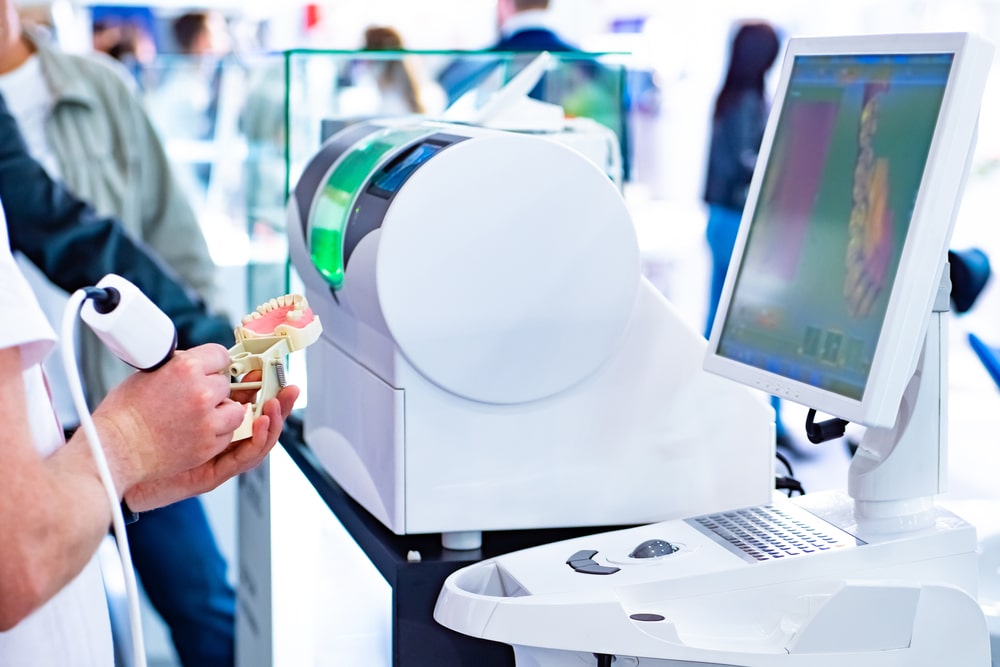
Digital radiography is an advanced form of X-ray imaging where digital sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. This technology produces high-quality images that can be viewed on a computer screen, stored digitally, and shared easily. The transition from traditional film to digital radiography has revolutionized dental practices, particularly in implant dentistry.
Key Uses of Digital Radiography in Implant Dentistry
Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
Digital radiography provides detailed images of the patient’s oral structures, including bone quality, density, and the condition of surrounding tissues. These images are crucial for determining whether a patient is a suitable candidate for dental implants. The clarity and precision of digital X-rays help in identifying any potential issues, such as bone loss or periodontal disease, that might affect implant placement.
Treatment Planning
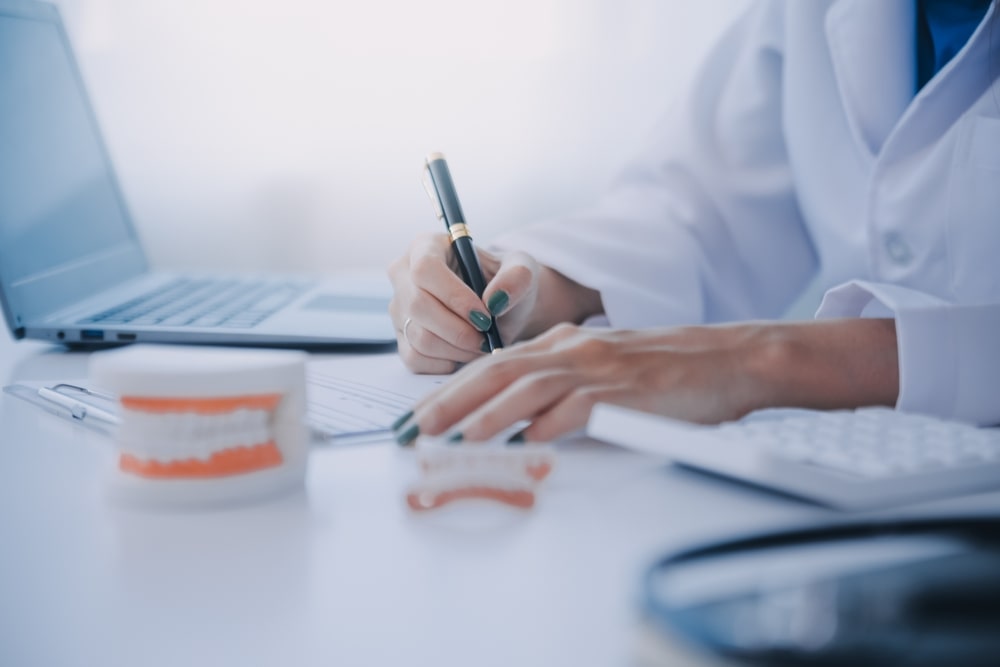
Accurate treatment planning is essential for the success of dental implants. Digital radiography allows dentists to create detailed and precise treatment plans. With the help of advanced software, practitioners can simulate the implant placement, ensuring optimal positioning and alignment. This technology also aids in selecting the appropriate size and type of implant, tailored to the patient’s unique anatomical structure.
Guided Implant Surgery
Digital radiography plays a critical role in guided implant surgery. By combining digital images with computer-aided design (CAD) software, dentists can fabricate surgical guides. These guides ensure that implants are placed with high precision, minimizing the risk of complications and enhancing the overall success rate of the procedure.
Post-Operative Assessment
After the implant placement, digital radiography is used to monitor the healing process and assess the integration of the implant with the bone. Regular imaging allows for early detection of any issues, such as infection or implant mobility, enabling timely intervention. This continuous monitoring ensures the long-term success of the implant.
Patient Education and Communication
One of the significant advantages of digital radiography is its ability to enhance patient communication. High-quality images can be easily shared with patients, helping them understand their oral health condition and the proposed treatment plan. Visual aids are powerful tools in educating patients about the implant process, fostering trust and confidence in the procedure.
Advantages of Digital Radiography
Enhanced Image Quality
Digital radiography produces images with superior clarity and detail compared to traditional film X-rays. This enhanced image quality allows for more accurate diagnoses and treatment planning.
Reduced Radiation Exposure
Digital radiography requires significantly less radiation than conventional film-based X-rays. This reduction is particularly beneficial for patients who require multiple images over time.
Immediate Image Availability
Unlike traditional X-rays, which require time for film development, digital images are available instantly. This immediacy allows for quicker decision-making and streamlined workflows within the dental practice.
Digital Storage and Sharing
Digital images can be easily stored in electronic health records and shared with other dental professionals as needed. This capability facilitates collaboration and continuity of care, especially in complex cases requiring multidisciplinary approaches.
Environmentally Friendly
Digital radiography eliminates the need for chemical processing and film disposal, making it a more environmentally sustainable option.
Communication with Dental Labs
Digital radiography in implant dentistry greatly enhances communication with dental labs, leading to more efficient and accurate collaboration. High-quality digital images can be easily shared with lab technicians, providing them with precise visual data about the patient’s oral anatomy. This seamless transfer of information allows for the creation of custom implant components and prosthetics that fit perfectly and meet the specific needs of the patient. The benefits of this enhanced communication include reduced turnaround times, fewer adjustments, and improved overall outcomes. By ensuring that both the dental practice and the lab are working with the same detailed information, digital radiography helps streamline the entire implant process, leading to higher-quality results and greater patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Digital radiography has become an indispensable tool in implant dentistry, offering numerous benefits that enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and safety of dental implant procedures. From initial assessment and treatment planning to guided surgery and post-operative care, this technology plays a vital role in ensuring successful outcomes for patients. As dental practices continue to embrace digital advancements, the future of implant dentistry looks promising, with improved patient experiences and better clinical results.